Understanding the meaning of neurodivergence can help us appreciate the unique ways in which individuals process the world around them. Let’s explore what it means to be neurodivergent and how it differs from being neurotypical.
Key Takeaways
- Neurodivergent Meaning: Refers to individuals whose brains function differently than what is considered “normal.”
- Conditions Under Neurodivergence: Includes ADHD, autism, dyslexia, and more.
- Support: Open dialogue and understanding are crucial in supporting neurodivergent individuals.
Neurodivergent Meaning: Neurodivergence describes when someone’s brain develops or functions differently from what is typically expected. This term encompasses various conditions, such as ADHD, autism, and dyslexia, highlighting the unique strengths and challenges of those whose brains work differently from the norm.
Table of Contents
Neurodivergent vs Neurotypical
What’s the difference between people who are and aren’t neurodivergent, to begin with? The word for people who aren’t neurodivergent is neurotypical. That means their strengths and challenges aren’t affected by any kind of difference that changes how their brains work. Additionally, neurotypical individuals reach developmental milestones at a time and age that’s considered standard for most people.
Conversely, the term neurodivergent describes people whose brain differences affect how their brain works. Someone who is neurodivergent behaves, thinks, and learns differently compared to those who are not. Basically, this term refers to an individual whose brain functions differently from what we consider “normal”. That means they have different strengths and challenges from people whose brains don’t have those differences. The possible differences can include medical disorders, learning delays, and other conditions. For these people, differences in the brain affect how they develop, behave, and process information.
Read more: Is ADHD Neurodiversity?
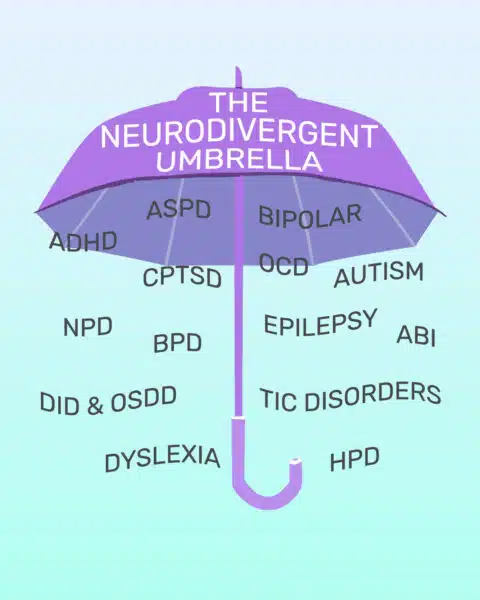
Common Neurodivergent Conditions
Many conditions fall under the neurodivergent umbrella. Some of the most common are:
- Tourette’s syndrome.
- Down syndrome.
- Epilepsy.
- Depression.
- Dyscalculia.
- Dysgraphia.
- Dyslexia.
- Dyspraxia.
- Intellectual disabilities.
- Prader-Willi syndrome.
- Sensory disorders.
- Social anxiety.
- Williams syndrome.
Read more: How to Co-Parent Kids with Special Needs
Goally | Apps To Support Child Development
Looking for fun ways to help your child learn life skills? Try Goally! The Goally tablet comes with award-winning learning apps and video classes to help kids develop the skills they need to become independent with FUN & evidence-based practices.

Our apps teach executive function, language, emotional regulation, finger dexterity skills, and more.
As your child develops new skills, you can increase the difficulty level of the tasks in the app to challenge and motivate them even further. This helps your child grow and progress at their own pace, while also keeping them engaged and excited about their development.
Supporting Neurodivergent Individuals
So, how can you, as parents, friends, or family members, provide your support? It’s as simple as sparking a chat. Yep, promoting open and honest dialogue with your loved ones can make a world of difference. By understanding their viewpoint, you’re not just offering a helping hand, but also celebrating their distinctive talents and contributions. Remember, every conversation counts when it comes to showing our support and appreciation for the neurodivergent community.
Helpful Resources
FAQ’s About Being Neurodivergent
Is ADHD neurodivergent? Yes. ADHD is commonly misdiagnosed as a mental health condition. However, the symptoms and behaviors associated with ADHD result from brain differences, so ADHD is a neurodivergent condition. Is OCD neurodivergent? Yes. OCD is a form of anxiety disorder. The compulsions result from higher activity levels in certain parts of the brain. Because of brain functioning differences, individuals with OCD are not considered Is anxiety neurodivergent? Sometimes. Some people experience fleeting moments of anxiety, while others have chronic anxiety. Anxiety can shape how individuals think or behave in everyday life over an extended period. Is bipolar neurodivergent? Yes. People with borderline personality disorder have brain differences that affect how they think and behave, allowing for its classification as a neurodivergent condition. Is BPD neurodivergent? Yes. People with borderline personality disorder have brain differences that affect how they think and behave. Is PTSD neurodivergent? Yes. Because of the extensive effects that PTSD has on the brain after someone experiences trauma, is called an acquired neurodivergent condition. Is neurodiversity a disability? If someone has a neurodivergent condition, it's not necessarily a disability. Though, some people who have conditions that affect their day-to-day life benefit from accommodations at work or school.
This post was originally published on 11/18/2022. It was updated on 08/26/2024.
Emily is a seasoned blog writer for Goally, leveraging her extensive background in child psychology and special education to provide valuable insights and resources for parents. Her commitment to understanding and addressing the unique needs of these children, combined with her expertise in educational strategies, makes her a credible and empathetic voice for families.