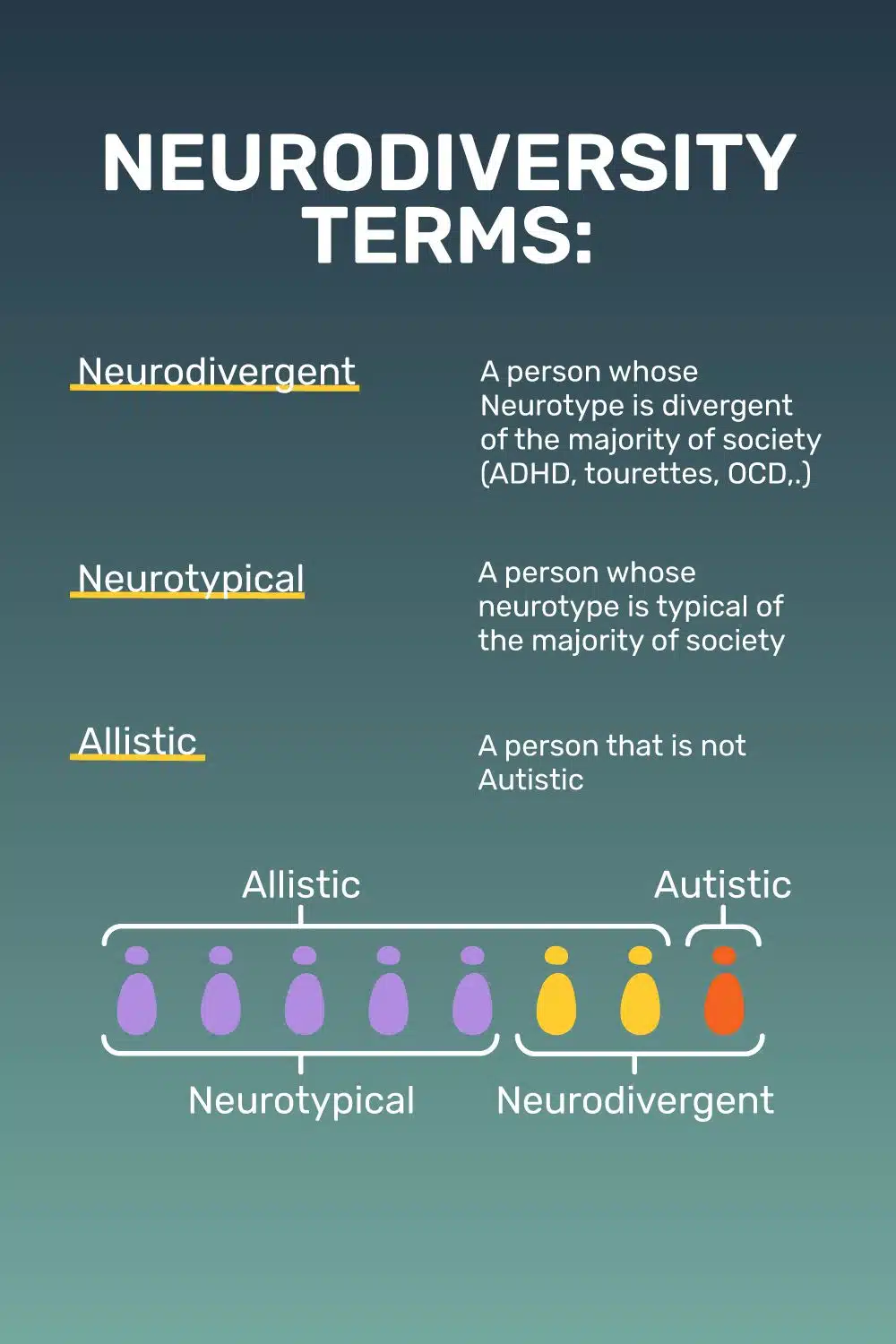
Neurotypical and neurodivergent individuals exhibit different patterns of behavior and experience the world in distinct ways. Understanding the symptoms associated with these conditions can help foster greater empathy and create a more inclusive society.
|
Neurotypical (NT) |
Neurodivergent (ND) |
| Characteristics |
Typical social interaction and communication skills.
Conformity to established social norms and expectations.
Less sensitivity to sensory stimuli.
Linear and focused thinking patterns. |
Varied social interaction and communication styles.
Non-conformity to social norms and expectations.
Heightened sensitivity to sensory stimuli.
Diverse and unconventional thinking patterns. |
Recognizing and appreciating the diverse range of symptoms associated with neurotypical and neurodivergent individuals can promote inclusivity and acceptance. By understanding these differences, we can build more accommodating environments and foster meaningful connections with people who have diverse neurological experiences.
This post was originally published on Feb. 15, 2023. It was updated on Nov. 18, 2023.