Meet Susie, a curious and imaginative young girl who loves to explore the world around her. With child-centered education, Susie’s learning journey becomes an exciting adventure tailored to her interests. Here’s how child-centered education benefits Susie:
- Customized Learning: Susie gets to choose topics she’s passionate about, like animals or space, making her lessons captivating and relatable.
- Hands-On Projects: Susie engages in exciting projects, like building a model rocket or creating an animal habitat, sparking her creativity and critical thinking skills.
- Collaborative Learning: Susie teams up with classmates to solve puzzles or create a play, boosting her social skills and teamwork abilities.
- Individual Attention: Susie’s teacher recognizes her unique learning style, providing personalized support and guidance tailored to her needs.
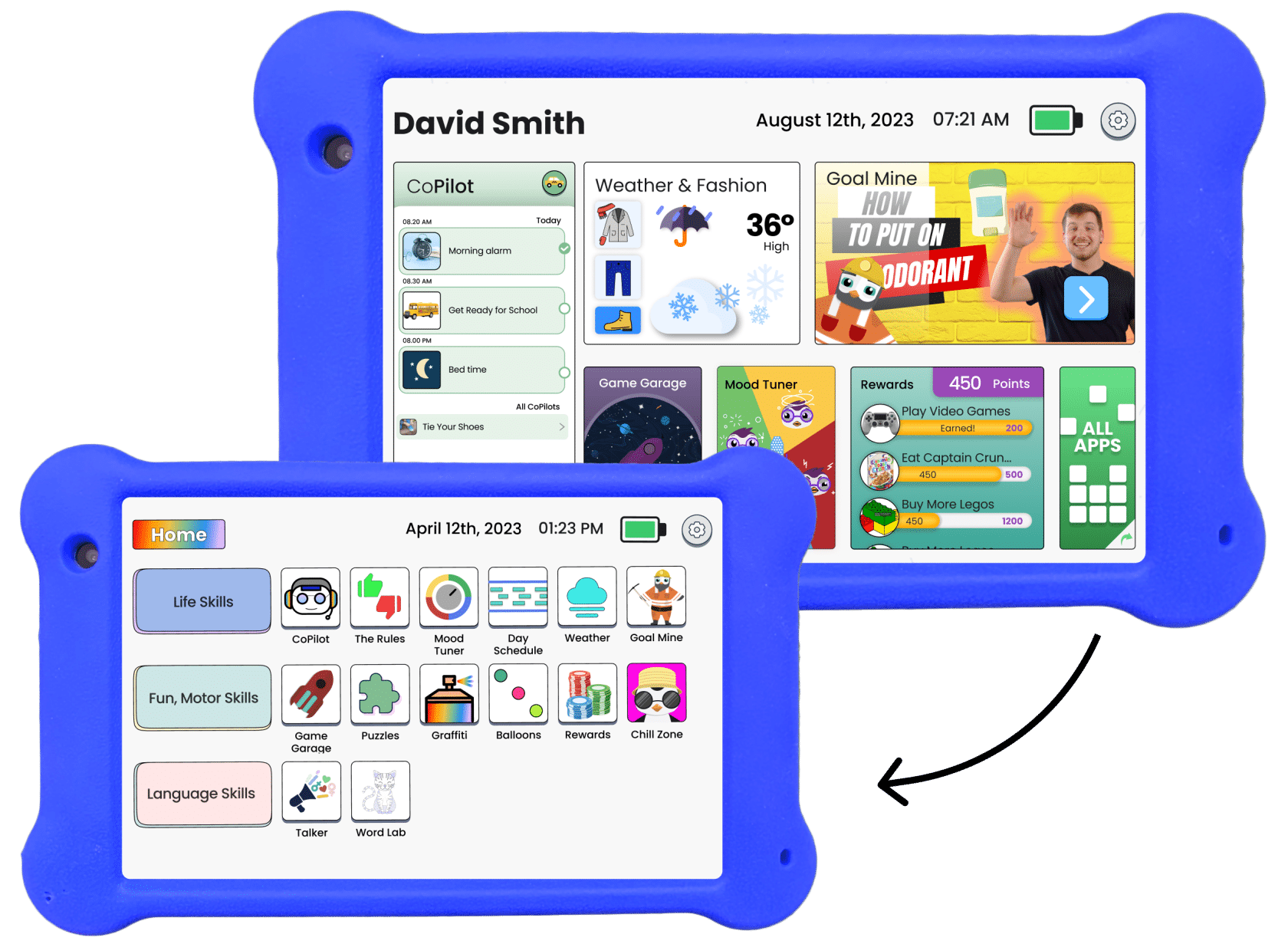
- Fun Learning Tools: Susie explores educational apps on Goally, discovering new worlds through interactive games, language learning, and visual schedules.
With child-centered education, Susie thrives as an active learner, embracing challenges, and developing a lifelong love for learning.