When it comes to math, many kids struggle with a tricky duo: math anxiety and working memory. As a parent, you may be searching for ways to support your child through these challenges. This comprehensive guide will shed light on the relationship between math anxiety and working memory, offer useful strategies to help your child cope with anxiety, and provide tips to boost their working memory for a more enjoyable and successful math experience.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Connection: Math Anxiety and Working Memory
Math anxiety is an emotional response to math-related tasks, often resulting in fear, worry, and stress. This anxiety can have a negative impact on a child’s working memory – the temporary storage and processing of information necessary for learning and problem-solving. To understand how these two factors interact, let’s consider the following points:
| Working memory and math skills | Impact of anxiety on working memory | A vicious cycle |
|---|---|---|
| Strong working memory skills are essential for successfully completing math tasks. For example, when solving a multi-step problem, children need to hold and manipulate numbers and operations in their minds. | Anxiety can hinder working memory by taking up valuable cognitive resources, making it more difficult for kids to focus on the task at hand. This means that when a child is experiencing math anxiety, their working memory capacity may be compromised. | Unfortunately, this combination can create a self-perpetuating cycle. As math anxiety increases, working memory performance may decline, making it even more challenging for kids to succeed in math-related tasks, which in turn exacerbates anxiety. |

Strategies to Manage Math Anxiety
Helping your child cope with math anxiety is crucial for improving their working memory and overall math performance. Here are some practical strategies to consider:
- Normalize anxiety: Reassure your child that experiencing anxiety is normal and that many people feel anxious about math. Encourage open communication about their feelings and provide a supportive environment for them to share their concerns.
- Break tasks into smaller steps: Breaking down complex math problems into smaller, manageable steps can make them less intimidating and help reduce anxiety.

Read more: What is Working Memory & How Does it Relate to Autism?
In addition to the above strategies, there are more ways to help your child manage their math anxiety:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Teach your kid the practice of relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, to help them calm down when they feel anxious during math tasks.
- Reframe negative thoughts: Encourage your child to challenge and reframe negative thoughts about their math abilities. Help them replace self-defeating thoughts with positive, constructive ones.
- Provide positive reinforcement: Praise your child’s efforts and progress, not just their results. This will help them develop a growth mindset and boost their confidence in their math abilities.
Tips to Strengthen Working Memory
Improving your child’s working memory can greatly enhance their math performance and reduce anxiety. Here are some tips to help them build stronger working memory skills:
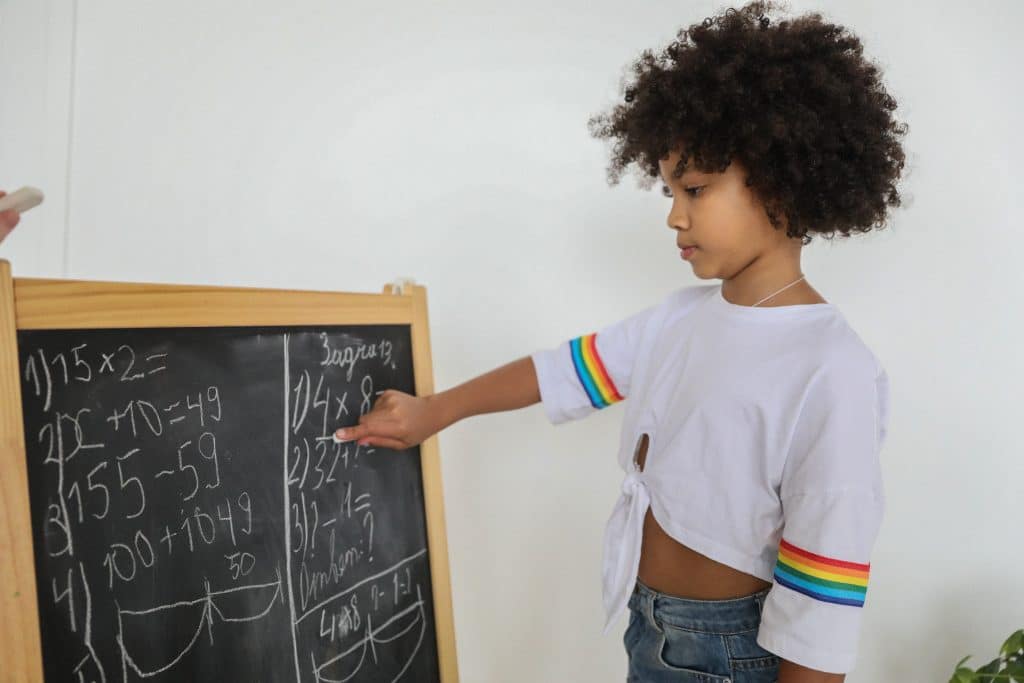
Read more: 7 Working Memory Examples in Kids
- Encourage active learning: Engage your child in activities that require them to use their working memory, such as solving puzzles, playing memory games, or participating in hands-on learning experiences.
- Teach visualization techniques: Encourage your child to create mental images of the information they are trying to remember. Visualization can be particularly helpful in understanding complex mathematical concepts and improving working memory.
Moreover, there are other strategies you can use to strengthen your child’s working memory:
- Develop routines: Establishing daily routines and habits can help kids with thinking and learning differences to organize their thoughts and minimize the cognitive load on their working memory.
- Provide accommodations: For kids who struggle with working memory, consider providing accommodations such as extra time on tests, access to reference materials, or the use of technology tools designed to support working memory.
- Seek professional support: If your child continues to struggle with working memory despite your efforts, consider seeking the guidance of a professional, such as a psychologist or learning specialist, who can provide targeted interventions and support.
Goally | Apps To Support Child Development
Looking for fun ways to help your child learn life skills? Try Goally! The Goally tablet comes with award-winning learning apps and video classes to help kids develop the skills they need to become independent with FUN & evidence-based practices.

Our apps teach executive function, language, emotional regulation, finger dexterity skills, and more.
As your child develops new skills, you can increase the difficulty level of the tasks in the app to challenge and motivate them even further. This helps your child grow and progress at their own pace, while also keeping them engaged and excited about their development.
Moving Forward
Understanding the relationship between math anxiety and working memory is essential for supporting your neurodivergent child’s learning journey. By implementing strategies to manage anxiety and strengthen working memory, you can help your child overcome challenges and foster a positive attitude towards math. Remember, every child is unique, and finding the right combination of strategies may take time and patience. But with your support and encouragement, your child can develop the skills and confidence needed to succeed in math and beyond.
This post was originally published on 05/14/2023. It was updated on 09/05/2023.

Goally
We help parents teach their kids life skills, like doing bedtime and morning independently. Backed by science, we incorporate evidence-based practices and expert-informed designs in all of our apps and content.






